Comparing real-time (RT-CGM) and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring (IS-CGM)* in adults with type 1 diabetes (ALERTT1): a 6-month, prospective, multicenter, randomised controlled trial†
Background
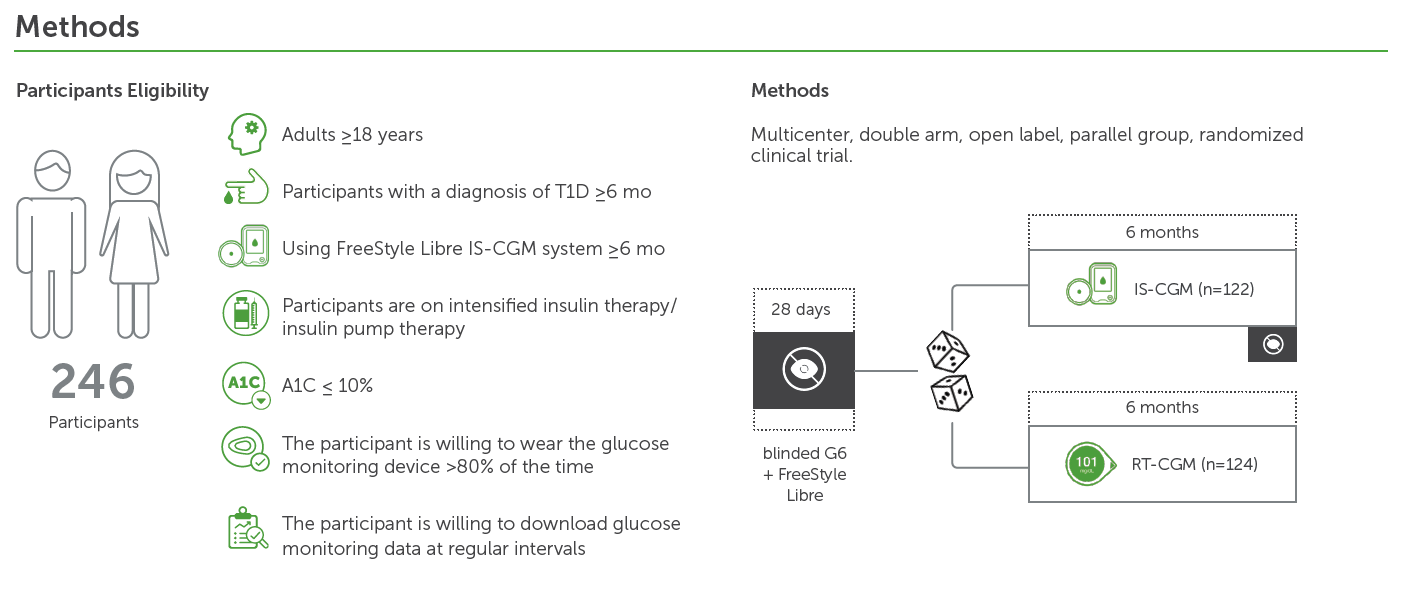
People with type 1 diabetes (T1D) can continuously monitor their glucose levels on demand with IS-CGM, or in real time with RT-CGM.
However, it is unclear whether switching from IS-CGM to RT-CGM with alert functionality offers additional benefits.
Objective
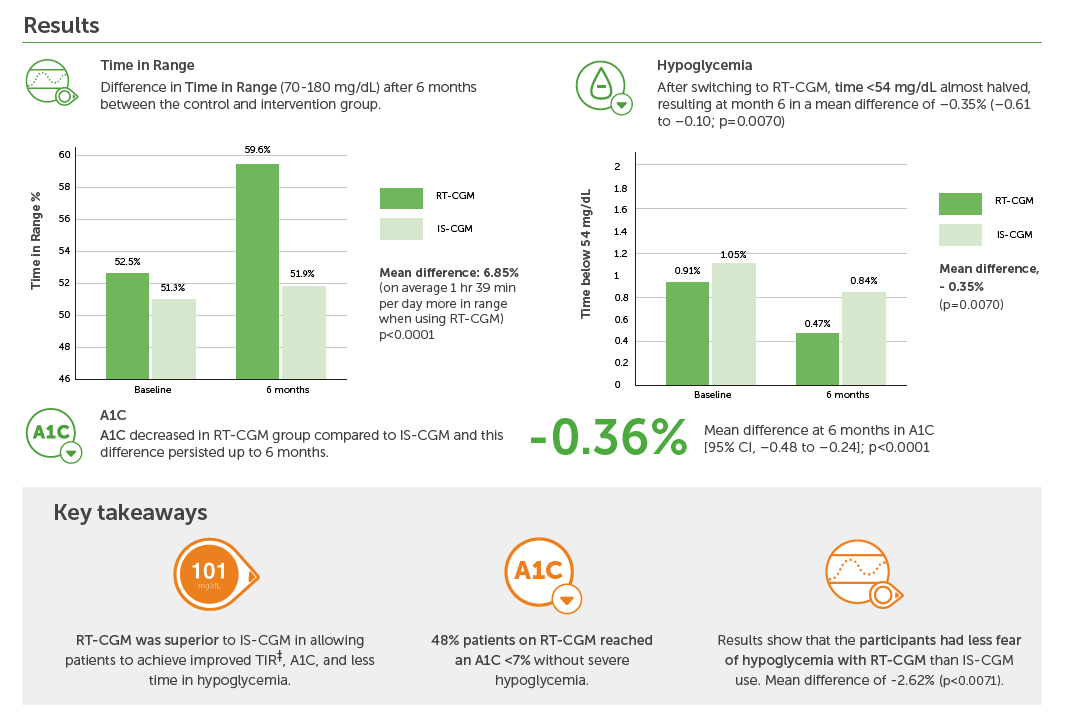
Evaluate if use of switching from IS-CGM to RT-CGM with alert functionality improves glycemic outcomes and quality of life in adults with T1D.
Margaretha M Visser, Sara Charleer, Steffen Fieuws, et al.
Published Online June 2, 2021 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00789-3
*IS-CGM used in this trial was FreeStyle Libre 14 day system
† This clinical summary of the published article is interpreted by Dexcom
‡ Recommendations from the International Consensus on Time in Range, 2019 recommend individualized glycemic targets for high risk and/or older adults with a focus on reducing the percentage of time spent less than 70 md/dL and preventing excessive hyperglycemia.
1. Comparing real-time and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes (ALERTT1): a 6-month, prospective, multicentre, randomised controlled trial
Visser, Margaretha M et al. The Lancet, Volume 397, Issue 10291, 2275 - 2283
Related Content
Topic: Behavior Change, Type 2 Diabetes, Lifestyle Modification Key question: Could glucose sensor use lead the individual to make significant dietary or activity changes, or perhaps encourage optimal...
Topics: Type 2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular Outcomes, Behavior Change Key question: What are the potential benefits of widening the application of glucose sensors in type 2 diabetes? Research Spotlight:...
