Six-Month Randomized, Multicenter Trial of Closed-Loop Control in Type 1 Diabetes
The efficacy and safety of the Control-IQ hybrid closed-loop system, powered by Dexcom G6, was evaluated in a multi-centered, randomized, and unblinded study.1 The researchers randomized 168 participants with type 1 diabetes (T1D), ages 14-71, 2:1 to the Control-IQ system or sensor-augmented pump therapy. The primary endpoint of the study was percent time in range (TIR; 70-180 mg/dL). Over the six months of the trial, the following outcomes were observed in the Control-IQ users:
-
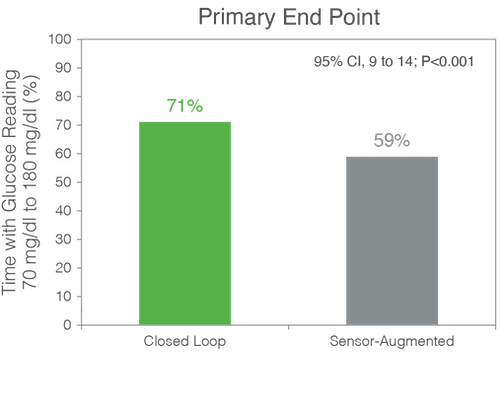
The mean (±SD) percent TIR increased in the closed-loop group from 61±17% at baseline to 71±12% during the 6 months and remained unchanged at 59±14% in the control group (mean adjusted difference, 11 percentage points; P<0.001).
• This correlates to a mean increase in TIR of ~2.6 hours daily.
• The greatest difference in the median percentage of time in the target range occurred at 5 a.m. (89% in the closed-loop group vs. 62% in the control group).
-
The mean difference in percent time >180 mg/dL was −10 percentage points (P<0.001), a difference that amounted to 2.4 hours per day less time spent in hyperglycemia for the closed-loop group.
-
Mean difference in percent time spent <70 mg/dL was −0.88 percentage points (P<0.001) between the closed-loop and control groups, a difference that amounted to 13 minutes per day less time spent in hypoglycemia for the closed-loop group.
-
Percent TIR and percent time <70 mg/dL consistently favored the closed-loop system across a broad range of baseline characteristics, including age, sex, body-mass index, income, educational level, insulin pump or injection use, previous use of a continuous glucose monitor, and A1C.
-
Median percent CGM use over the 6 months of the trial was 97% (IQR, 96-98) in the closed-loop group and 96% (IQR, 90-97) in the control group. In the closed-loop group, the median percentage of time the system was in closed-loop mode was 90% (IQR, 86-94) and was consistent throughout the 6 months.
The glycemic benefits that users achieved after a month of using on the Control-IQ system were sustained over the entire six months. The mean time in range was 71% for the study group, which meets internationally endorsed consensus targets for time in range.2
The Control-IQ system significantly increases time in range
1 Brown SA, et al. Six-Month Randomized, Multicenter Trial of Closed-Loop Control in Type 1 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;381(18):1707-17.
2 Battelino T, et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(8):1593-1603.
Related Content
Topic: Behavior Change, Type 2 Diabetes, Lifestyle Modification Key question: Could glucose sensor use lead the individual to make significant dietary or activity changes, or perhaps encourage optimal...
Topics: Type 2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular Outcomes, Behavior Change Key question: What are the potential benefits of widening the application of glucose sensors in type 2 diabetes? Research Spotlight:...
